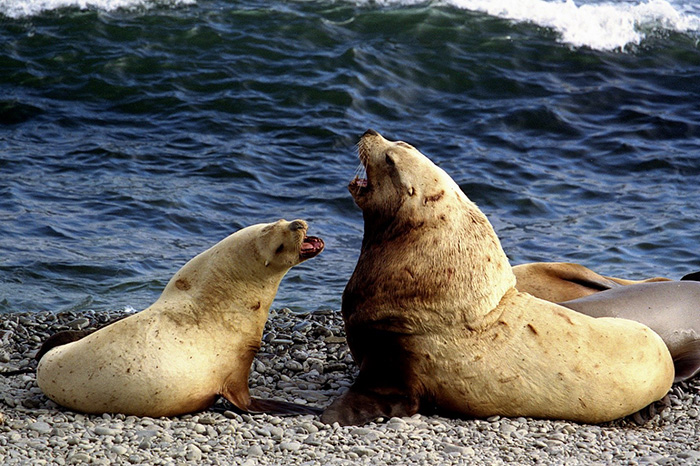
The American Mink Neovison vison Schreber, 1777
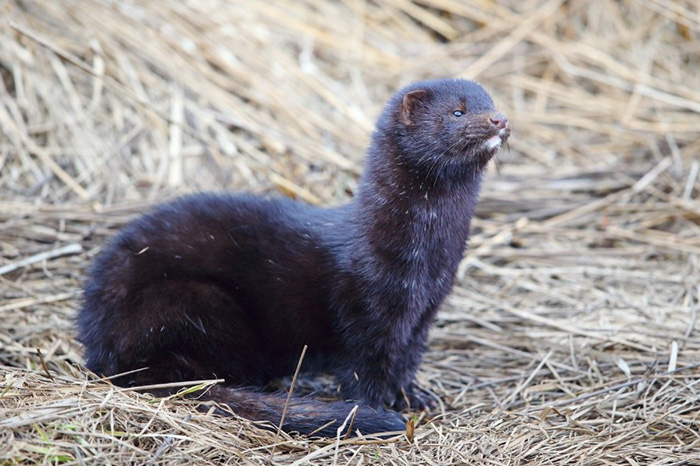

The American mink escaped from the fur farm and acclimatized itself on Bering Island. Photograph by Eugene Mamaev
The body length of adult males is 35-54 cm, the weight is up to 2 kg, but females are smaller. The newborns weigh 7-14 gm.
The natural habitat of the species is North America. It was imported to the USSR for breeding in captivity in 1928, and since 1933 they began to acclimatize the American mink. For now the species has populated the majority of Russian territory except for the Far North. In the European part it goes even beyond the Arctic Circle.
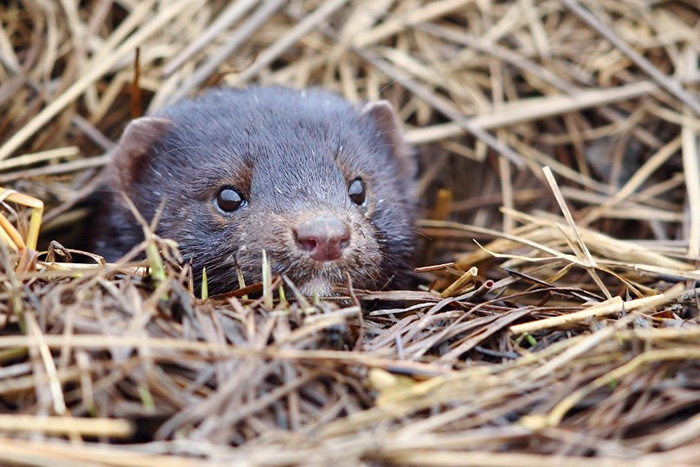

The American mink lives in burrows, dug on the coasts of water bodies. Photograph by Eugene Mamaev
The ration consists of coastal, aquatic and forest animals: crustaceans, insects, shelfish, fish, birds, mouse-like rodents.
The rut lasts from late February to early April. The gestation period is 36-80 days, with the latent stage of 1-7 weeks. Minks bear from 1 to 9 or even more cubs. Lactation lasts for 2-2,5 months. Females become sexually mature at 1 year, males at 1,5 years. Life expectancy is up to 10 years.
Minks live in the coastal zone, on the banks of water bodies, where they place their burrows. They can swim under water up to 30 m, and dive to a depth of 4 m. During years that are rich in food they can lead a sedentary life, and during years with bad feeding conditions roam from place to place. During the day they can pass up to 5 km.
Bering Island is inhabited by minks, which escaped from the fur farm during 60-s of the XXth century.
Nowadays the American mink is found all over the island, both in inland waters – rivers and lakes, and the seacoast. It does not avoid neighborhood with human, it’s rather typical for the species. For example, females brood right under the houses on the territory, where people live temporarily.
The ecology of minks on the island is studied rather poorly. The mink eats marine mollusks and other marine invertebrates, which it gets during low tides on the littoral and among marine emissions; it catches fish in numerous rivers and lakes of the island, and also catches mouse-like rodents (the northern red-backed vole and the brown rat). Minks were also noticed hunting waterfowls. Besides, minks can feed on carrion, for example, driven ashore marine mammals. The Arctic fox is an enemy of the mink, which can crush it, if it has a chance.
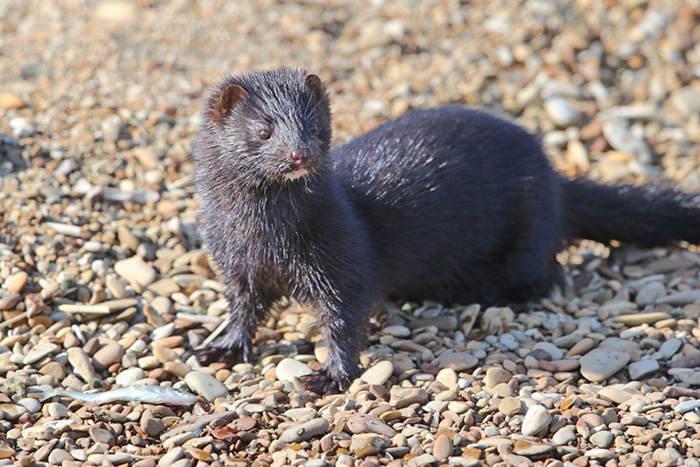

The American mink with the prey –three-spined stickleback. Photograph by Eugene Mamaev
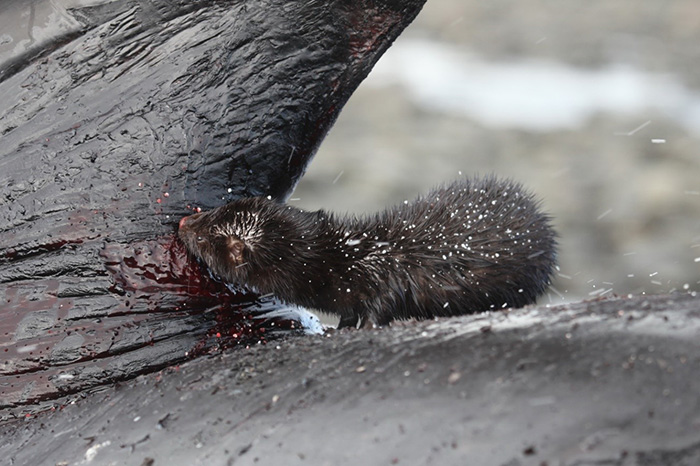

Should an opportunity arise the American mink eats cetacean driven ashore. Photograph by Eugene Mamaev
The population of the species on the island is unknown.